⚠️ Before disassembly, make sure to power off the phone.
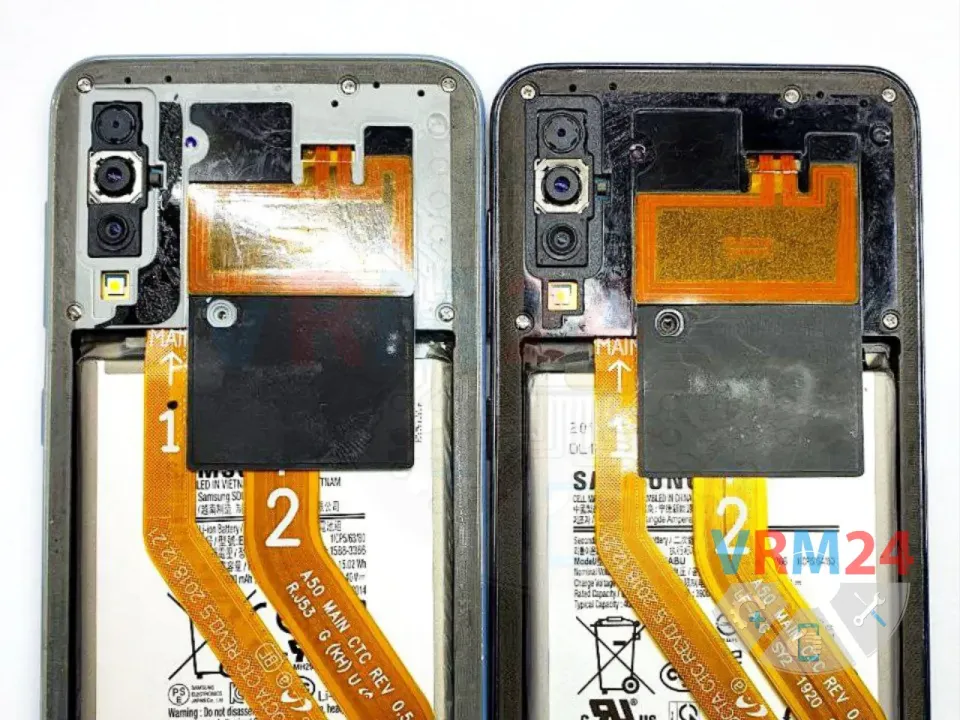
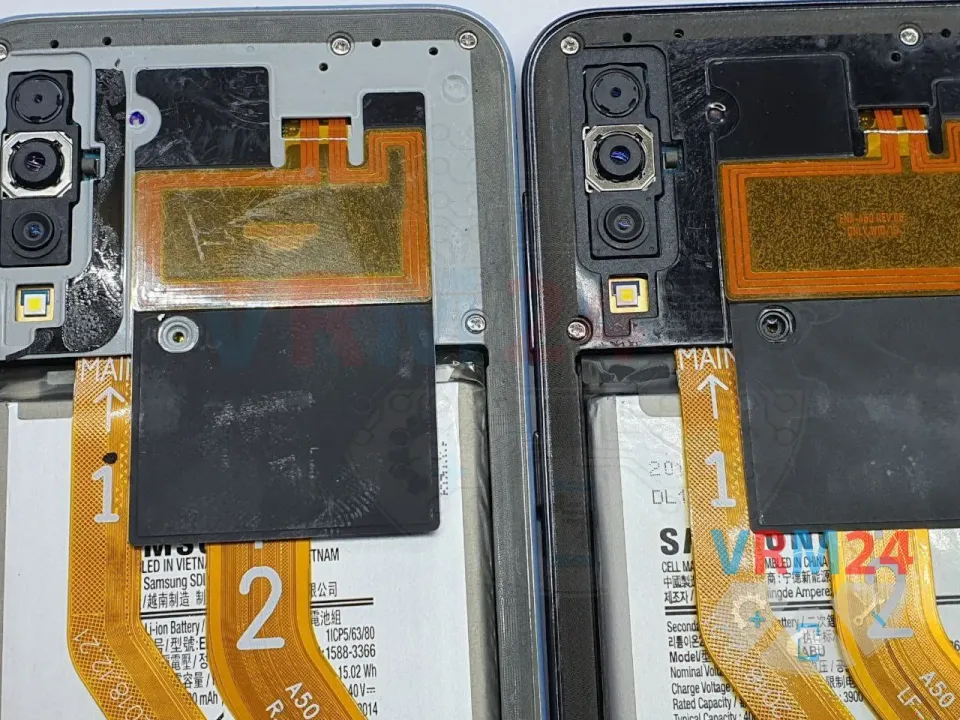
We encountered two identical Samsung A50 devices with similar audio-related failures:
First device: Microphone and speaker not working.
Second device: Crackling noise and distortion during calls.
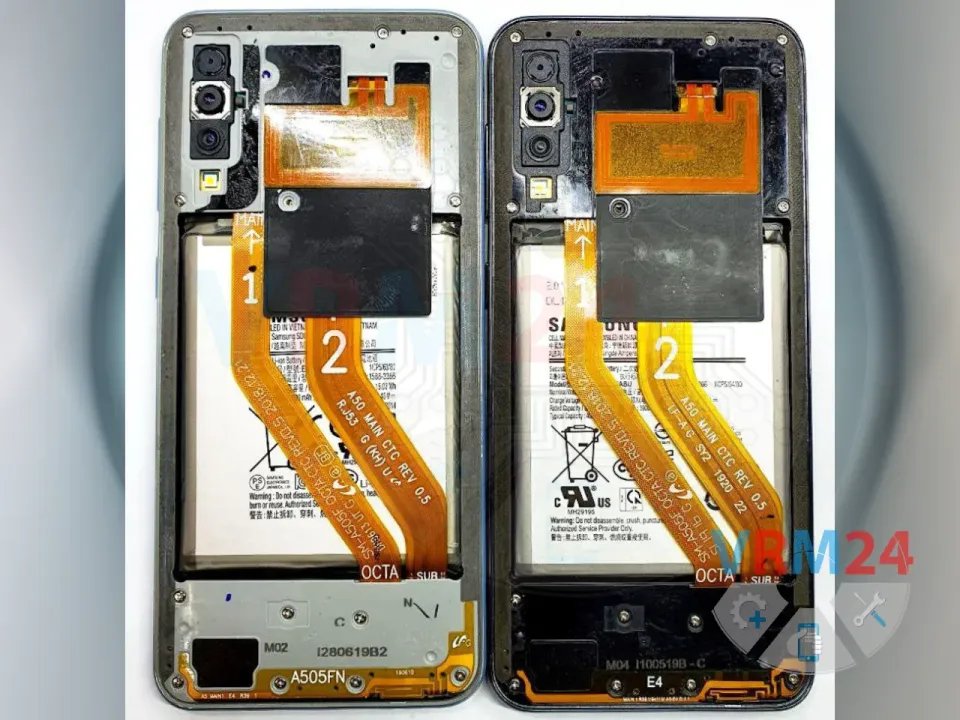
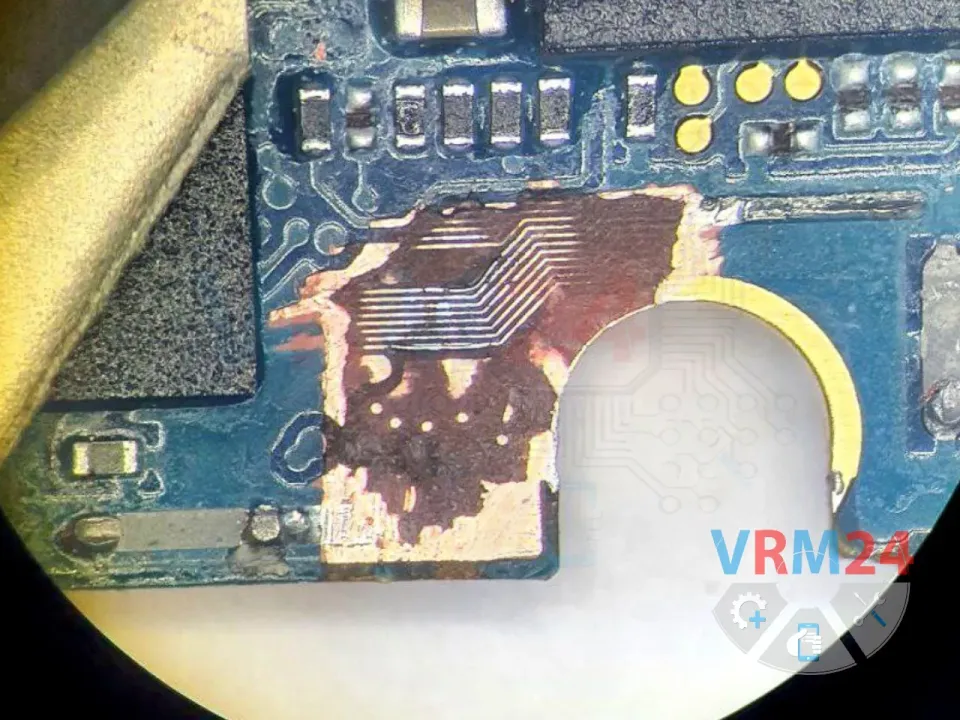
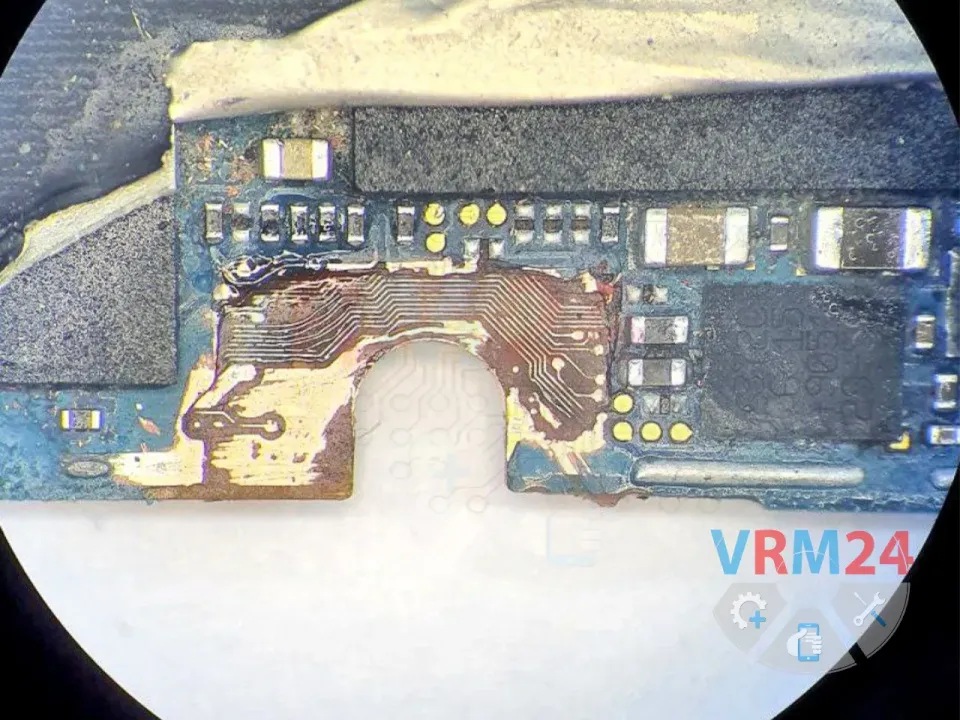
This is a very common issue in this model. After a drop or impact, the audio codec traces under the metal frame (near the screw) often get damaged, leading to sound problems.
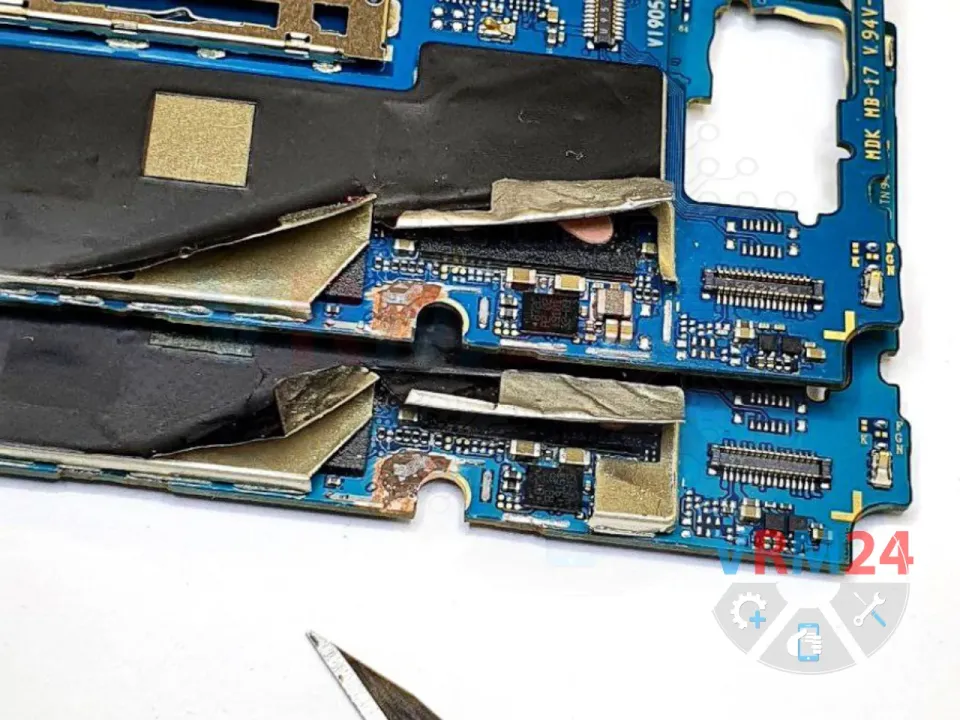
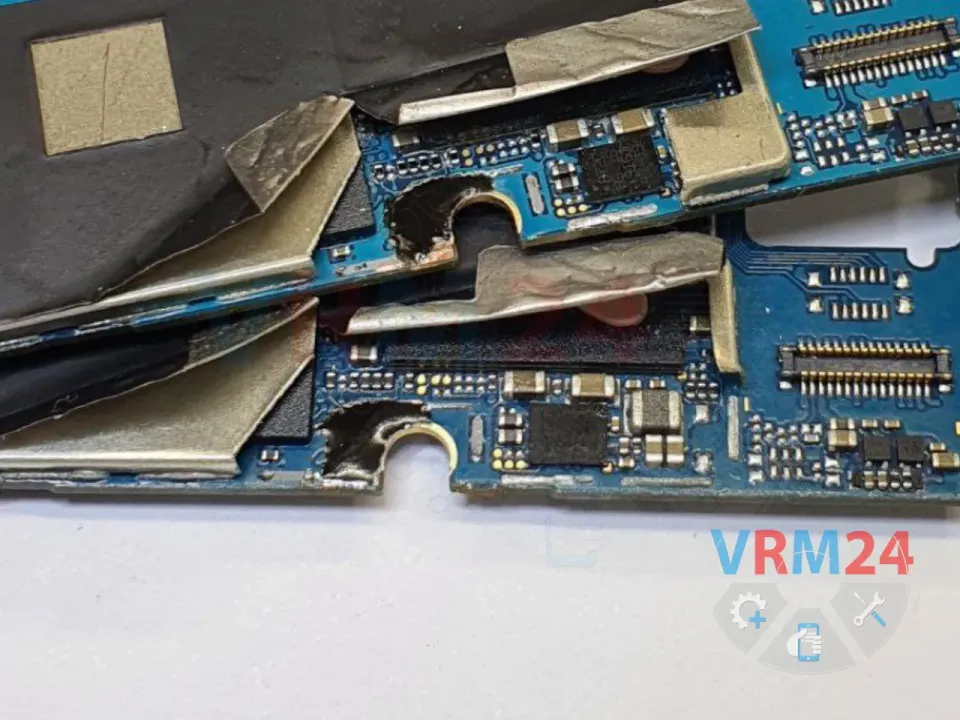
🔧 Carefully scrape away the PCB substrate under the frame to expose the second layer, where the damaged audio traces to the codec are located.
🔬 Under a microscope, we repair the broken traces using thin copper wire jumpers to restore connectivity.
⚠️ Sometimes, traces break on the opposite side too, requiring more extensive scraping to access and repair them.
📸 (See photo below for reference—showing the audio traces in the second layer under the frame.)
🛡️ After repairs, apply UV-curable solder mask to secure and insulate the jumper wires, preventing future shorts or breaks.
✅ After testing, reassemble the smartphones—but do NOT reinstall the center screw!
🚫 Why? This screw is the main culprit—when tightened, it puts pressure on the PCB, making it prone to trace fractures upon impact.
If you have a question, ask us, and we will try to answer in as much detail as possible. If this article was helpful for you, please rate it.